Deciding between forced air vs central air systems? Each has its benefits and costs, which can impact your home’s comfort and budget. This article breaks down the differences, helping you choose the best option.
Key Takeaways
- Forced air systems provide dual functionality for both heating and cooling, utilizing the same ductwork for efficient temperature control throughout the home.
- Central air systems focus solely on cooling indoor spaces through a closed circuit of refrigerated air, which may require separate heating solutions for year-round comfort.
- Choosing the right HVAC system involves evaluating needs, budget, and existing infrastructure, with considerations for installation costs and long-term maintenance requirements.
Understanding HVAC systems can be overwhelming with all the technical jargon involved. At Quality Heating, Cooling, Plumbing & Electric, we pride ourselves on being Milwaukee’s trusted experts in HVAC installation. Our goal is to make sure you feel confident and informed when choosing a new system. With our experienced team on your side, you can trust that you’re making the best decision for your home.
Understanding Forced Air Systems
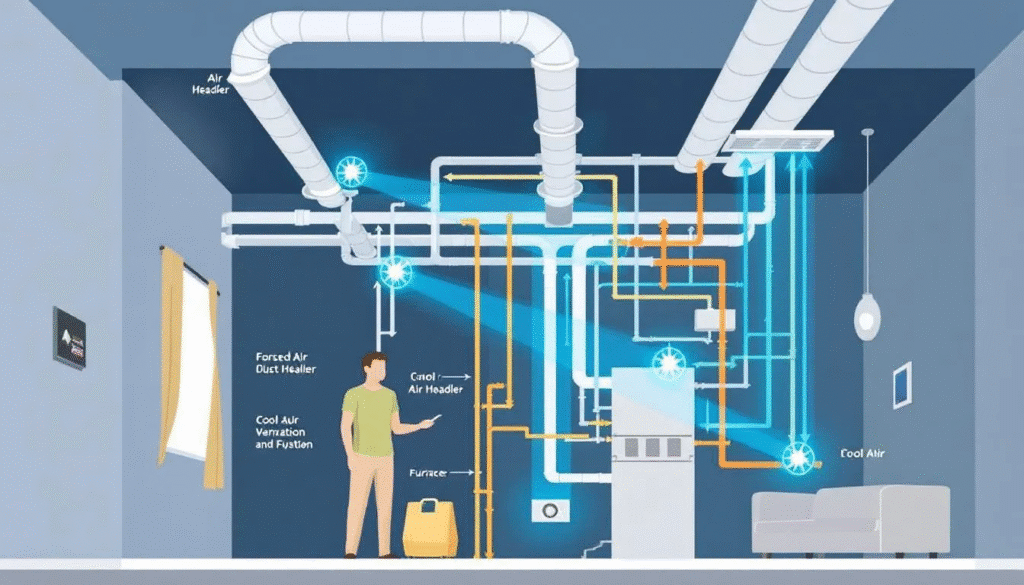
A forced air system, an HVAC system, delivers temperature-controlled air via vents and ducts. Key features include:
- Incredible efficiency at maintaining a consistent indoor temperature, making them popular among homeowners
- Circulation of air through ducts and vents
- Provision of heated or cooled air as needed
- Distribution method that ensures consistent temperature control in every room
Forced air systems are versatile, capable of both heating and cooling your home. This dual functionality is one of the primary reasons they are so widely used. These systems use a single network of ducts and forced air system’s vents to switch efficiently between heating and cooling modes, providing year-round comfort with a heating system, central air and forced, and the same forced air system.
The following sections will delve into how forced air systems manage heating and cooling systems.
How Forced Air Heating Works
Forced air heating primarily relies on:
- Furnaces or heat pumps to generate heat.
- A furnace that heats the air.
- A blower that distributes the heated air through ducts, warming your home.
- A thermostat that regulates the process, allowing you to set and maintain your desired indoor temperature.
- Induction motors that enhance the system’s efficiency by extracting exhaust gases and improving heat exchange.
The flexibility of forced air systems is another significant advantage. They can operate independently or in conjunction with central air, providing a seamless heating solution without requiring additional infrastructure.
Whether using gas furnaces or a heat pump, the principle is the same: heated air is efficiently distributed through ducts and vents, keeping every room warm during colder months.
How Forced Air Cooling Works
Forced air systems excel in cooling as well. These systems work in tandem with central air conditioning units to cool your home. The air conditioner uses evaporator coils to cool the air, absorbing indoor heat and releasing it outside. This cooled air is then distributed through the same ductwork used for heating, ensuring even cooling throughout your home.
The beauty of forced air cooling lies in its efficiency. Using the same ducts for heating and cooling eliminates the need for separate infrastructure, reducing installation costs and simplifying maintenance. Whether it’s the peak of summer or the dead of winter, a forced air system ensures your home remains comfortable by delivering temperature-controlled air exactly where it’s needed.
Central Air Conditioning Systems Explained
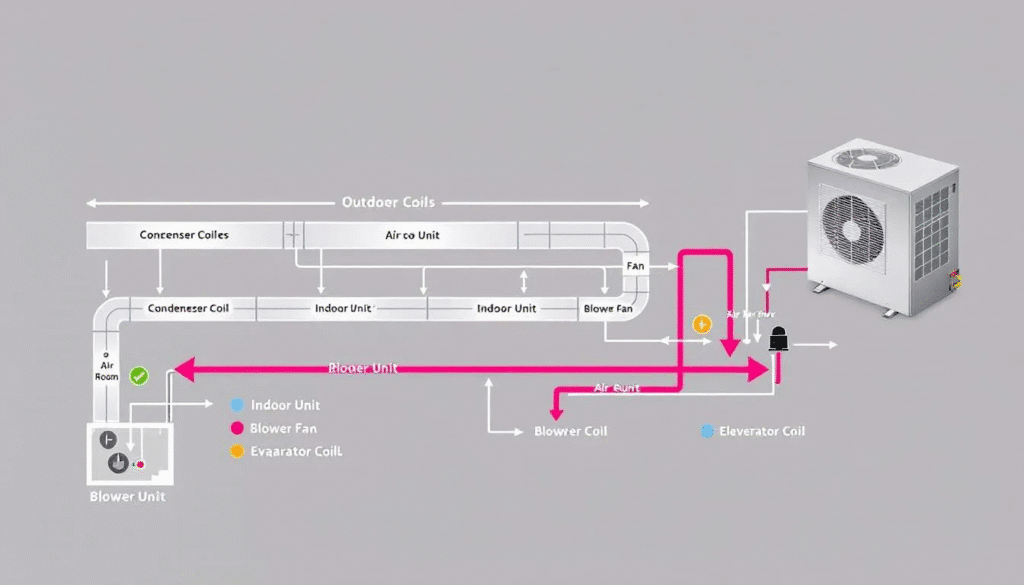
Central air conditioning systems are designed to cool an entire house. They also effectively cool larger buildings. These systems operate using a closed circuit of refrigerated air, which cools your home efficiently and effectively. Central air systems are popular in hot climates, where consistent cooling is essential for comfort.
Key components of a central air system include:
- Vents
- Ducts
- A plenum These components work together to distribute cool air throughout your home. The average installation cost for a central air system ranges from $5,000 to $10,000, with a typical lifespan of 15 to 20 years vs central air.
The following sections will explore the components and cooling process of central air systems in detail.
Components of Central Air Systems
Central air conditioning systems rely on several key components to function effectively:
- The air conditioner or heat pump cools the air.
- An existing blower system circulates the cooled air.
- The evaporator coil in the indoor unit cools the air before distribution by absorbing heat from the indoor air.
This process allows the cooling system to deliver cool, refreshing cold air in a closed loop to every room.
The outdoor unit plays an equally important role. It expels the absorb heat outside, completing the refrigeration cycle. Together, these components ensure that your home remains consistently cool, even during the hottest months of the year.
Recognizing these components highlights the complexity and efficiency of central air systems.
How Central Air Cools Your Home
Central air conditioning systems cool your home by distributing cooled air through a network of ducts. The central air conditioning unit uses a refrigerant to remove heat from indoor air, absorbing and expelling heat as it transitions between gas and liquid states. This process is regulated by a thermostat, ensuring that your home maintains a consistent, comfortable temperature.
The cool air circulates through ducts to each room, ensuring uniform cooling. This even distribution eliminates hot spots and ensures that every part of your home remains comfortable. The use of existing ductwork from the forced-air system simplifies installation and reduces costs.
One of the significant benefits of central air systems is their ability to improve indoor air quality. These systems filter and circulate air, removing dust, allergens, and pollutants, thus creating a healthier indoor environment. Thus, central air systems keep your home cool and improve overall indoor air quality.
Key Differences Between Forced Air and Central Air
Recognizing the key differences between forced air and central air systems is vital for making an informed decision. While both systems use ducts to distribute air, their primary functions and mechanisms differ significantly. Central air systems focus solely on cooling, while forced air systems provide both heating and cooling capabilities. This versatility makes forced air systems popular for homeowners seeking an all-in-one solution. Understanding the nuances of air vs central systems can further aid in selecting the right option.
Another critical key difference lies in the heating and cooling mechanisms. Forced air systems use furnaces or heat pumps to generate heat, while central air systems rely on a closed circuit of refrigerated air to cool your home. Choosing between these systems often depends on existing ductwork, which can significantly impact installation costs and complexity.
Heating and Cooling Capabilities
Forced air systems are notable for providing both heating and cooling through the same ductwork. This dual functionality makes them efficient and cost-effective for many homeowners. Whether it’s a hot summer day or a chilly winter night, a forced air system can keep your home at the perfect temperature.
Central air systems, on the other hand, are primarily designed to cool indoor spaces by removing and expelling heat. Though they excel at maintaining a cool indoor environment, they lack heating capabilities. Homeowners may need to pair central air hvac systems with separate heating solutions to achieve year-round comfort.
Ductwork and Air Distribution
Both systems use a common ductwork system to distribute air throughout a home. This shared infrastructure offers several benefits:
- Simplifies installation and maintenance, especially if your home already has ductwork.
- Central air systems use the same ducts as furnaces.
- Ensures efficient air distribution system and consistent cooling.
The use of shared air ducts also means that both systems can potentially improve better indoor air quality by filtering out dust and allergens. However, proper maintenance and regular cleaning of ductwork are essential to prevent pollutant circulation and maintain optimal performance.
Pros and Cons of Forced Air Systems
Forced air systems offer several advantages:
- Reduced energy consumption compared to traditional heating methods.
- Ability to provide both heating and cooling through the same ductwork, making them versatile.
- Air filters that enhance indoor air quality by removing dust and allergens.
However, there are potential drawbacks to consider. Forced air systems can be expensive to operate if they are inefficient or poorly maintained. Regular maintenance keeps the system efficient and prevents the circulation of allergens and dust.
Despite these challenges, the lower repair costs and improved indoor air quality involve replacing forced air systems as a compelling option for many homes.
Pros and Cons of Central Air Systems
Central air conditioning systems ensure consistent cooling throughout a home, eliminating temperature variations and hot spots. Controlling the temperature from a central unit or remotely offers homeowners greater flexibility and comfort. Central air systems can also increase a home’s market value, making them desirable for potential buyers.
However, installing central air systems can be disruptive due to significant structural modifications. The initial cost of installation is also higher compared to other cooling options, which can be a barrier for some homeowners. Yet, the long-term benefits of consistent cooling and improved indoor air quality often outweigh these initial challenges.
Choosing the Right HVAC System for Your Home
Selecting the right HVAC system involves considering your specific needs, budget, existing infrastructure, and personal preferences. Space constraints are significant, as central air systems require adequate outdoor space for compressors and indoor ductwork. Homeowners should carefully evaluate their options to determine which system best meets their needs.
For homes with existing ductwork, a forced air system can be a cost-effective choice that enhances home value. If your home is frequently humid, a forced-air HVAC system might be more suitable due to its humidity control. Consulting a knowledgeable HVAC contractor ensures proper installation and maintenance, leading to optimal performance.
Cost Considerations for Installation and Maintenance
Installing a new HVAC system typically costs:
- Between $5,000 and $12,500, depending on installation complexity and the chosen system
- An additional $1,000 to $2,700 for ductwork, especially for homes without existing systems
- Up to $22,000 for comprehensive HVAC system replacements with upgrades
Consider both the initial cost and long-term maintenance expenses. Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping both forced air and central air systems functioning efficiently and preventing costly repairs. Annual maintenance and regular filter replacement or cleaning are crucial for optimal performance and reducing energy consumption.
High-efficiency models may increase higher upfront cost but lead to significant long-term savings through lower energy bills to ensure optimal performance and energy efficient operation. Evaluating these factors helps you make an informed decision balancing budget and comfort.
Tips for Finding a Quality HVAC Contractor
Finding a quality HVAC contractor ensures smooth professional installation and reliable performance. A qualified installer requires professional installation, ensuring correct setup, maximizing efficiency and lifespan. Consider a contractor’s experience and expertise in installing and servicing HVAC systems.
Get multiple quotes from contractors to compare prices and services. Inquire about labor and equipment warranties to ensure the best service and protection for your investment. The following subsections will provide additional tips on checking licensing and reading reviews.
Check Licensing and Certification
Verify a contractor’s credentials to ensure they are qualified for HVAC work. Confirming adherence to local licensing and certification requirements ensures legal operation and provides peace of mind.
Licensed contractors reduce the risk of subpar service and potential liability issues. It ensures the contractor meets industry standards and provides reliable, high-quality service.
Read Reviews and Get Recommendations
Customer reviews offer valuable insights into the quality and reliability of HVAC companies. Online reviews provide firsthand accounts, helping you gauge the service and expertise you can expect. Researching HVAC contractors’ reputations ensures you choose a reliable service provider.
Combining customer reviews with referrals provides a well-rounded view of prospective contractors. Personal recommendations offer detailed insights and highlight contractors with proven track records in your community. This approach helps you make an informed decision, ensuring your HVAC system is installed and maintained by trusted professionals.
Summary
Choosing between forced air and central air systems involves a careful consideration of your specific needs, budget, and existing home infrastructure. Forced air systems offer the advantage of providing both heating and cooling through the same ductwork, making them a versatile option for year-round comfort. They are also known for their energy efficiency and ability to enhance indoor air quality.
On the other hand, central air systems excel in providing consistent cooling throughout your home, eliminating temperature variations and improving indoor air quality. Although they require a higher initial investment and significant structural modifications, their long-term benefits, including increased home value, often outweigh these challenges.
Ultimately, the best HVAC system for your home depends on your unique circumstances and preferences. By understanding the pros and cons of each system, considering installation and maintenance costs, and working with a reputable HVAC contractor, you can make an informed decision that ensures your home remains comfortable and energy-efficient year-round.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between forced air and central air systems?
The main difference is that forced air systems offer both heating and cooling through the same ductwork, whereas central air systems are designed exclusively for cooling your home.
How do forced air systems improve indoor air quality?
Forced air systems improve indoor air quality by utilizing air filters that effectively remove dust, allergens, and other pollutants from the air. This filtration process creates a healthier living environment for occupants.
What factors should I consider when choosing an HVAC system?
When choosing an HVAC system, it’s essential to consider your specific needs, budget, existing home infrastructure, space constraints, and personal preferences. These factors will ensure you select a system that effectively meets your requirements.
How much does it cost to install a new HVAC system?
Installing a new HVAC system generally costs between $5,000 and $12,500, but total expenses can increase to around $22,000 if ductwork and upgrades are needed. It’s essential to consider these factors when budgeting for your new system.
Why is it important to verify a contractor’s licensing and certification?
Verifying a contractor’s licensing and certification is crucial as it confirms their qualifications and compliance with industry standards, minimizing the risk of poor service and liability issues. This step protects your investment and ensures the work is done safely and effectively.



0 Comments